A single day of sunbathing increases the risk of heart disease and harms the immune system.
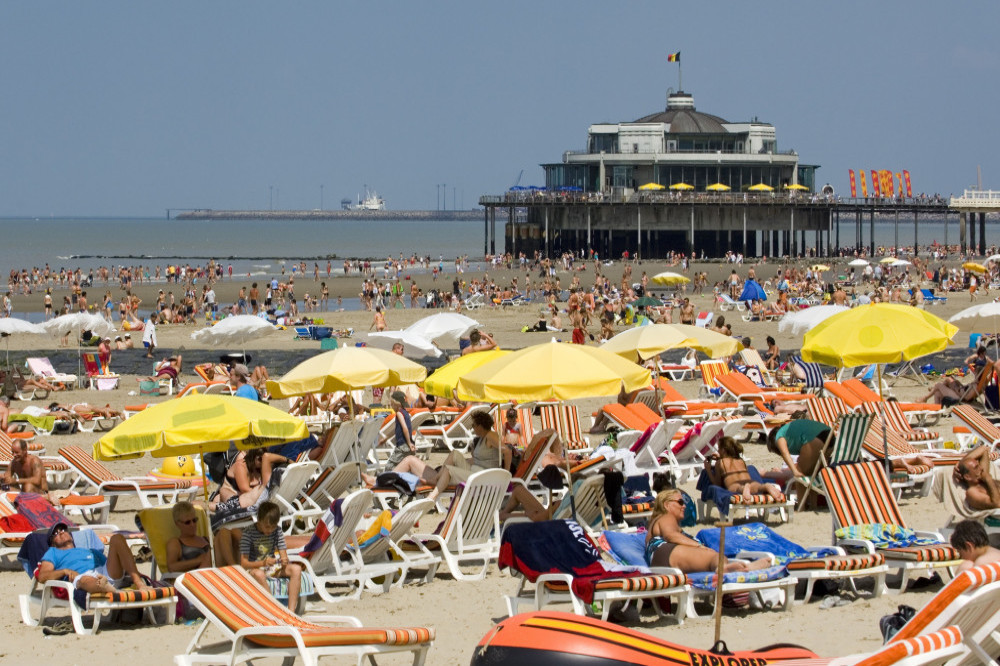

A day of sunbathing has plenty of health risks
Prolonged exposure to high temperatures is known to raise the risk of skin cancer and headaches but scientists have now found that it causes the release of inflammatory compounds that lead to internal damage through the build-up of plaque in the arteries - a telltale sign of heart disease.
The study of 624 adults - who had blood samples taken once during the summer months between May 2018 and September 2019 - also showed a six per cent drop in vital immune system cells known as B-cells, which enable the body to fight viruses and germs.
Professor Daniel Riggs, who led the study for the University of Louisville, said: "With rising global temperatures, the association between heat exposure and a temporarily weakened immune system is a concern because temperature and humidity are known to be important environmental drivers of infectious, airborne disease transmission.
"Thus, during the hottest days of summer people may be at higher risk of heat exposure, they may also be vulnerable to disease or inflammation."
Tagged in Sun Protection